一文让locust小白,变成性能测试老司机
locust介绍
locust是一款完全基于事件的负载测试工具,做性能测试使用的‘协程’方式,有webui图形界面、无图形界面、分布式等多种运行方式。
locust安装
首先,系统中安装python3.6及以上版本,确认安装好了pip
然后,安装locust,在终端中执行:
pip install locust
- 注意:
- Ⅰ 这种方式安装的是最新的 locust 版本,最新的版本已经是 locust 1.*
- Ⅱ 如果想安装低于 1.*的版本, 请使用
pip install locustio=版本号低于 1 的版本,包名称不一样。- Ⅲ 本文内容 locust的版本为 0.14.6, 所以请使用
pip install locustio==0.14.6
验证系统是否正常安装了locust,可以在终端中执行:
# 获取locust的帮助信息
locust --help
#或
# 查看locust的版本信息
locust -V
如果执行结果能够正常返回信息,说明当前系统已经安装好了locust工具。
locust脚本模板
对于一个初学者来说,是不是就期望能提供一个快速上手模板,套用模板就好呢?考虑到这点,我就在开篇,给大家一个模板:
import random
from locust import TaskSequence, HttpLocust, task, seq_task, between
# 定义一个任务类,这个类名称自己随便定义,类继承TaskSequence 或 TaskSet类,所以要从locust中,引入TaskeSequence或TaskSet
# 当类里面的任务请求有先后顺序时,继承TaskSequence类, 没有先后顺序,可以使用继承TaskSet类
class MyTaskCase(TaskSequence):
# 初始化方法,相当于 setup
def on_start(self):
pass
# @task python中的装饰器,告诉下面的方法是一个任务,任务就可以是一个接口请求,
# 这个装饰器和下面的方法被复制多次,改动一下,就能写出多个接口
# 装饰器后面带上(数字)代表在所有任务中,执行比例
# 要用这个装饰器,需要头部引入 从locust中,引入 task
@task
@seq_task(1) # 装饰器,定义有执行顺序的任务,扩展中的数字,从小到大,代表先后执行顺序
def regist_(self): # 一个方法, 方法名称可以自己改
url = '/erp/regist' # 接口请求的URL地址
self.headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"} # 定义请求头为类变量,这样其他任务也可以调用该变量
self.user = "locust_" + str(random.randint(10000, 100000))
self.pwd = '1234567890'
data = {"name": self.user, "pwd": self.pwd} # post请求的 请求体
# 使用self.client发起请求,请求的方法根据接口实际选,
# catch_response 值为True 允许为失败 , name 设置任务标签名称 -----可选参数
rsp = self.client.post(url, json=data, headers=self.headers, catch_response=True, name='api_regist')
if rsp.status_code == 200:
rsp.success()
else:
rsp.failure('regist_ 接口失败!')
@task # 装饰器,说明下面是一个任务
@seq_task(2) # 顺序任务装饰器,说明下面的任务,第二个执行
def login_(self):
url = '/erp/loginIn' # 接口请求的URL地址
data = {"name": self.user, "pwd": self.pwd}
rsp = self.client.post(url, json=data, headers=self.headers,
catch_response=True) # 使用self.client发起请求,请求的方法 选择post
self.token = rsp.json()['token'] # 提取响应json 中的信息,定义为 类变量
if rsp.status_code == 200 and rsp.json()['code'] == "200":
rsp.success()
else:
rsp.failure('login_ 接口失败!')
@task # 装饰器,说明下面是一个任务
@seq_task(3) # 顺序任务装饰器,说明下面的任务,第三个执行
def getuser_(self):
url = '/erp/user' # 接口请求的URL地址
headers = {"Token": self.token} # 引用上一个任务的 类变量值 实现参数关联
rsp = self.client.get(url, headers=headers, catch_response=True) # 使用self.client发起请求,请求的方法 选择 get
if rsp.status_code == 200:
rsp.success()
else:
rsp.failure('getuser_ 接口失败!')
# 结束方法, 相当于teardown
def on_stop(self):
pass
# 定义一个运行类 继承HttpLocust类, 所以要从locust中引入 HttpLocust类
class UserRun(HttpLocust):
task_set = MyTaskCase # 定义固定的 task_set 指定前面的任务类名称
wait_time = between(0.1, 3) # 设置运行过程中间隔时间 需要从locust中 引入 between
'''
运行:
在终端中输入:locust -f 被执行的locust文件.py --host=http://被测服务器域名或ip端口地址
也可以不指定host
命令执行成功,会提示服务端口,如:*:8089
此时,则可通过浏览器访问机器ip:8089,看到任务测试页面
'''
有了这个模板,以后用locust,基本上就是可以为所欲为啦。
如果你还不满足,可以继续往下看,我们来增强一下。
增强
脚本增强,那就要看你对python的运用能力。我们经常拿locust来做性能测试,所以增强就是增强性能测试方面的使用,我们可以在终端中,执行locust --help看下它的帮助信息
C:\Users\pc>locust --help
usage: locust [-h] [-H HOST] [--web-host WEB_HOST] [-P PORT] [-f LOCUSTFILE]
[--csv CSVFILEBASE] [--csv-full-history] [--master] [--slave]
[--master-host MASTER_HOST] [--master-port MASTER_PORT]
[--master-bind-host MASTER_BIND_HOST]
[--master-bind-port MASTER_BIND_PORT]
[--heartbeat-liveness HEARTBEAT_LIVENESS]
[--heartbeat-interval HEARTBEAT_INTERVAL]
[--expect-slaves EXPECT_SLAVES] [--no-web] [-c NUM_CLIENTS]
[-r HATCH_RATE] [-t RUN_TIME] [--skip-log-setup] [--step-load]
[--step-clients STEP_CLIENTS] [--step-time STEP_TIME]
[--loglevel LOGLEVEL] [--logfile LOGFILE] [--print-stats]
[--only-summary] [--no-reset-stats] [--reset-stats] [-l]
[--show-task-ratio] [--show-task-ratio-json] [-V]
[--exit-code-on-error EXIT_CODE_ON_ERROR] [-s STOP_TIMEOUT]
[LocustClass [LocustClass ...]]
Args that start with '--' (eg. -H) can also be set in a config file
(~/.locust.conf or locust.conf). Config file syntax allows: key=value,
flag=true, stuff=[a,b,c] (for details, see syntax at https://goo.gl/R74nmi).
If an arg is specified in more than one place, then commandline values
override config file values which override defaults.
positional arguments:
LocustClass
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-H HOST, --host HOST Host to load test in the following format:
http://10.21.32.33
--web-host WEB_HOST Host to bind the web interface to. Defaults to '' (all
interfaces)
-P PORT, --port PORT, --web-port PORT
Port on which to run web host
-f LOCUSTFILE, --locustfile LOCUSTFILE
Python module file to import, e.g. '../other.py'.
Default: locustfile
--csv CSVFILEBASE, --csv-base-name CSVFILEBASE
Store current request stats to files in CSV format.
--csv-full-history Store each stats entry in CSV format to
_stats_history.csv file
--master Set locust to run in distributed mode with this
process as master
--slave Set locust to run in distributed mode with this
process as slave
--master-host MASTER_HOST
Host or IP address of locust master for distributed
load testing. Only used when running with --slave.
Defaults to 127.0.0.1.
--master-port MASTER_PORT
The port to connect to that is used by the locust
master for distributed load testing. Only used when
running with --slave. Defaults to 5557.
--master-bind-host MASTER_BIND_HOST
Interfaces (hostname, ip) that locust master should
bind to. Only used when running with --master.
Defaults to * (all available interfaces).
--master-bind-port MASTER_BIND_PORT
Port that locust master should bind to. Only used when
running with --master. Defaults to 5557.
--heartbeat-liveness HEARTBEAT_LIVENESS
set number of seconds before failed heartbeat from
slave
--heartbeat-interval HEARTBEAT_INTERVAL
set number of seconds delay between slave heartbeats
to master
--expect-slaves EXPECT_SLAVES
How many slaves master should expect to connect before
starting the test (only when --no-web used).
--no-web Disable the web interface, and instead start running
the test immediately. Requires -c and -t to be
specified.
-c NUM_CLIENTS, --clients NUM_CLIENTS
Number of concurrent Locust users. Only used together
with --no-web
-r HATCH_RATE, --hatch-rate HATCH_RATE
The rate per second in which clients are spawned. Only
used together with --no-web
-t RUN_TIME, --run-time RUN_TIME
Stop after the specified amount of time, e.g. (300s,
20m, 3h, 1h30m, etc.png). Only used together with --no-
web
--skip-log-setup Disable Locust''s logging setup. Instead, the
configuration is provided by the Locust test or Python
defaults.
--step-load Enable Step Load mode to monitor how performance
metrics varies when user load increases. Requires
--step-clients and --step-time to be specified.
--step-clients STEP_CLIENTS
Client count to increase by step in Step Load mode.
Only used together with --step-load
--step-time STEP_TIME
Step duration in Step Load mode, e.g. (300s, 20m, 3h,
1h30m, etc.png). Only used together with --step-load
--loglevel LOGLEVEL, -L LOGLEVEL
Choose between DEBUG/INFO/WARNING/ERROR/CRITICAL.
Default is INFO.
--logfile LOGFILE Path to log file. If not set, log will go to
stdout/stderr
--print-stats Print stats in the console
--only-summary Only print the summary stats
--no-reset-stats [DEPRECATED] Do not reset statistics once hatching has
been completed. This is now the default behavior. See
--reset-stats to disable
--reset-stats Reset statistics once hatching has been completed.
Should be set on both master and slaves when running
in distributed mode
-l, --list Show list of possible locust classes and exit
--show-task-ratio print table of the locust classes'' task execution
ratio
--show-task-ratio-json
print json data of the locust classes'' task execution
ratio
-V, --version show program''s version number and exit
--exit-code-on-error EXIT_CODE_ON_ERROR
sets the exit code to post on error
-s STOP_TIMEOUT, --stop-timeout STOP_TIMEOUT
Number of seconds to wait for a simulated user to
complete any executing task before exiting. Default is
to terminate immediately. This parameter only needs to
be specified for the master process when running
Locust distributed.
图形界面相关
| 课选参数 | 用法解释 |
|---|---|
| -H HOST, --host HOST | 指定被测试的域名或ip地址及端口(两种方式都可以),要带上 前缀 |
| --web-host WEB_HOST | 运行locust的机器ip地址,浏览器访问时的ip(127.0.0.1\localhost\本机网络ip) |
| -P PORT, --port PORT, --web-port PORT | 指定locust运行的端口,默认时8089,可以通过这个参数,自定义端口 |
| -f LOCUSTFILE, --locustfile LOCUSTFILE | 指定locust运行的文件,如果文件名称为locustfile.py,可以不带这个参数 |
无图形界面相关:
| 可选参数 | 用法解释 |
|---|---|
| --no-web | **无头模式,**需要加 -c 和 -t 参数,启动时,根据配置直接运行 |
| -c NUM_CLIENTS, --clients NUM_CLIENTS | 无头模式中,运行的用户数,只能在无头模式时用 |
| -r HATCH_RATE, --hatch-rate HATCH_RATE | 性能测试时,生成用户的速率,只能在无头模式时用 |
| -t RUN_TIME, --run-time RUN_TIME | 无头模式中,运行的时长(30s秒、2m分钟、1h小时、1h30m),只能在无头模式时用 |
| --step-load | 启用步长加载 模式,做负载测试,需要有--step-clients 、--step-time |
| --step-clients STEP_CLIENTS | 步长加载模式中,加载的用户数,仅与 --step-load 一起用 |
| --step-time | 步长加载模式中,加载用的时间,仅与 --step-load 一起用 |
| --csv CSVFILEBASE, --csv-base-name CSVFILEBASE | 把运行结果写入指定前缀的csv文件中,默认2秒写一次,可以在py脚本种指定写入频率 |
| --csv-full-history | 将每个统计信息都写到 _stats_history.csv文件中 |
| --loglevel LOGLEVEL, -L LOGLEVEL | 日志级别,DEBUG/INFO/WARNING/ERROR/CRITICAL 默认为INFO |
| --logfile LOGFILE | 日志输出到文件,没有设置,日志将转到 stdout / stderr |
| --print-stats | 控制台输出 |
| --only-summary | 仅输出概要报告 |
分布式相关:
| 可选参数 | 用法解释 |
|---|---|
| --master | 设置为主控进程 |
| --master-bind-host MASTER_BIND_HOST | 绑定主控进程的ip地址,仅用于分布式的 --master |
| --master-bind-port MASTER_BIND_PORT | 绑定主控进程的port端口,仅用于分布式的 --master,默认端口为 5557 |
| --slave | 设置为助攻进程 |
| --master-host MASTER_HOST | 助攻机器连接的主控机器的ip地址,仅用于分布式的 --slave |
| --master-port MASTER_PORT | 助攻机器连接的主控机器的port地址,仅用于分布式的 --slave,默认情况主控端口5557 |
修改csv写入频率
import locust.stats
# 默认为 2 秒
locust.stats.CSV_STATS_INTERVAL_SEC = 1 # 自定义设置写入频率间隔为 1 秒
看了这个表格,这么多参数,是不是有些愣,不知道怎么用?
下面,我们就写三种,大家用的比较多的模式:
模式一:web图形界面模式。
Ⅰ. 在终端中执行:
locust -f 被执行的文件.py
py文件没有问题的话,将可以通过浏览器访问 http://localhost:8089 访问locust服务.
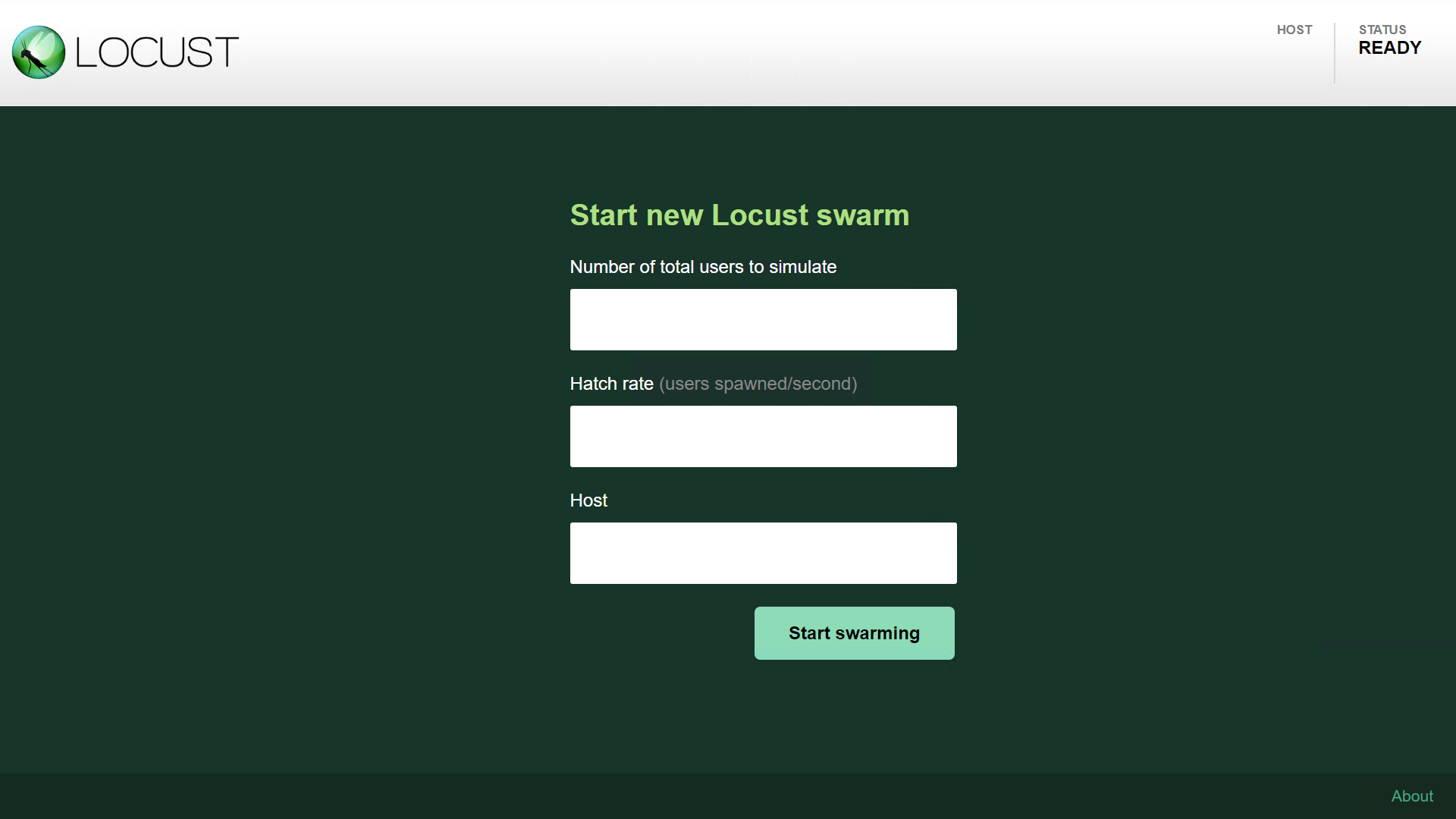
第1个"Number of total users to simulate" 填写的是 总共将运行的用户数;
第2个 "Hatch rate"每秒加载的用户数;
第3个 "Host",被测接口的域名或ip端口地址(带h
Start swarming , 启动
案例如图:
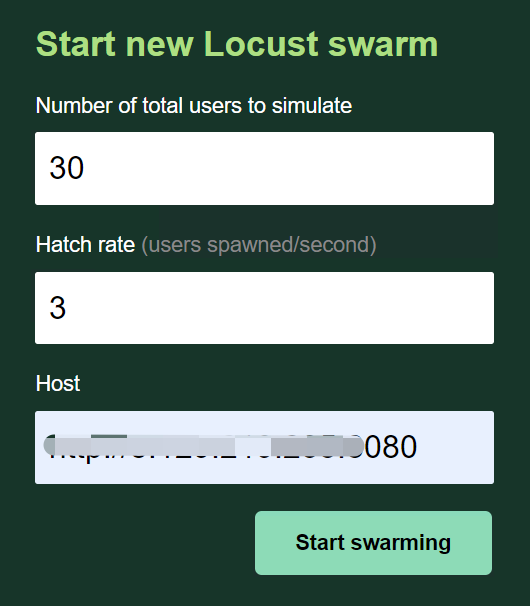
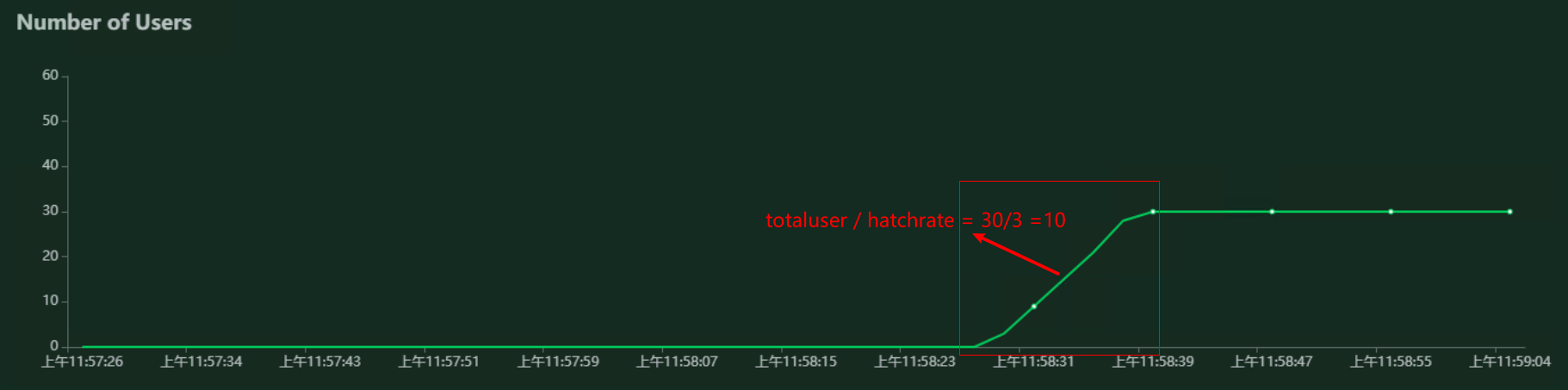
用5秒钟时间,启动30个用户,然后持续运行。
Ⅱ.当这个命令,再扩展一下,增加step-load,就可以增加步长压力,实现负载测试.
locust -f 被执行的文件.py --step-load
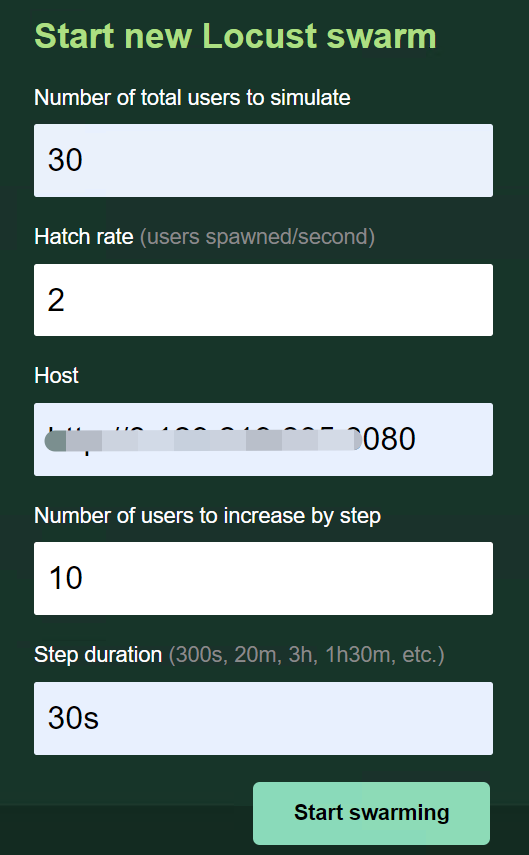
这样,访问 http://localhost:8089 时,就会出现步长的参数,如图:
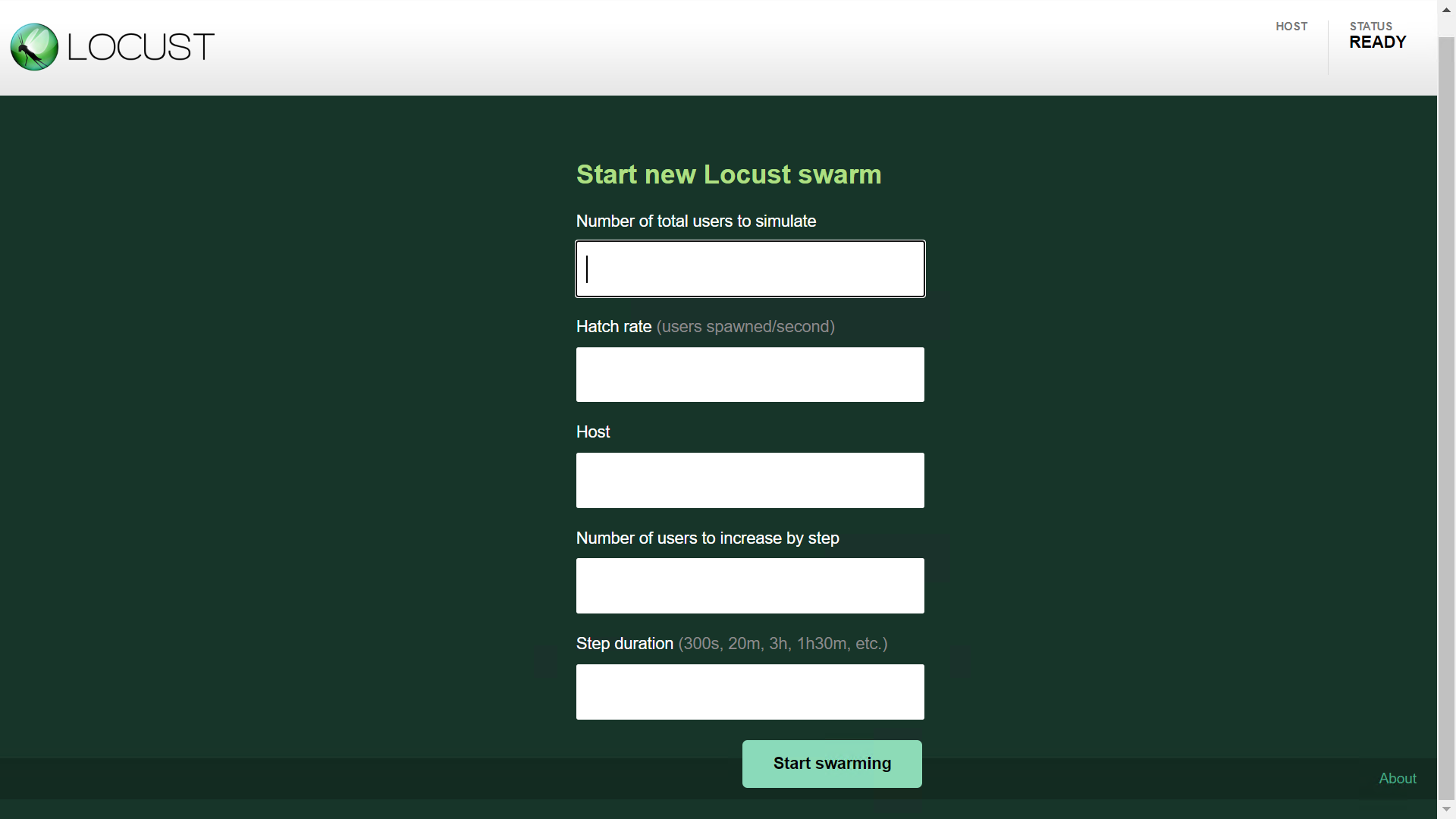
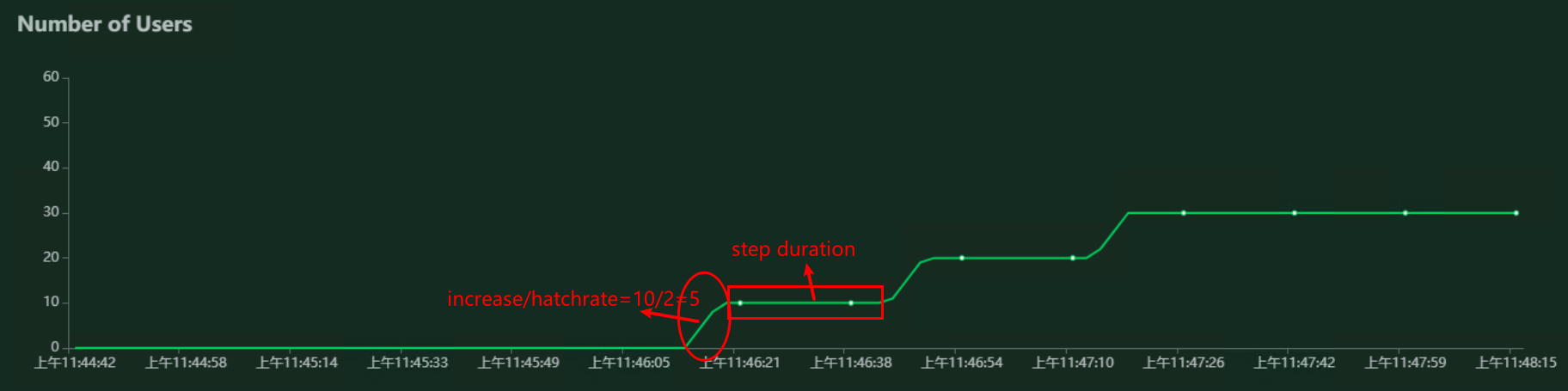
"Number of users to increase by step" 逐步增加用户数; "Step duration"步长持续运行时间
Ⅲ. 指定locust运行时的ip和端口
locust -f 被执行的文件.py --web-host 127.0.0.1 -P 8389
此时,浏览器的访问locust界面的地址和端口为 http://127.0.0.1:8389 ,这样,就手动修改了web界面的访问地址。当然,web-host的值,可以是(localhost, 127.0.0.1, 当前机器的ip地址)中任意一种。
注意:web-host的值,不能带http://
Ⅳ. 指定被测接口域名或ip端口地址
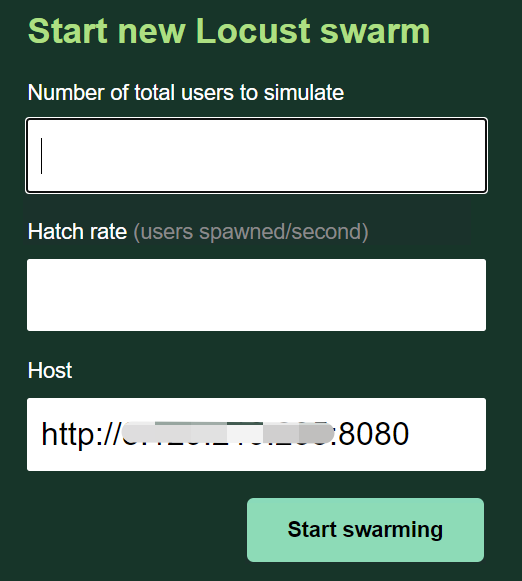
locust -f 被执行的文件.py --host=http://ip:8080
此时,浏览器访问 http://localhost:8089 时,页面中,已经自动带入了 Host值
模式二:无图形界面(无头模式)模式
无头模式,即无图形界面模式,不能通过浏览器访问页面来设置性能测试场景,只能通过命令中带参数来设置。参考命令如下:
locust -f 被执行的文件.py --no-web -c 30 -r 2 -t 2m --host=http://ip:8080 --csv=结果报告文件前缀
# --no-web 指名用无图形界面模式
# -c 指定运行的最大用户数,对应图形界面中的 Number of total users to simulate
# -r 指定每秒生成用户数,对应图形界面中的 Hatch rate
# -t 指定总共运行时长,因在无图形界面中,没有停止按钮,需要有这个参数才能到时间就停止,不然会一直运行下去,直到终端ctrl+c强行停止
# --host 指定被测服务器域名或ip端口地址
# --csv 指定输出结果到csv文件的前缀
这样,就会按照设置的参数,运行,到达运行时长自动停止,同时把测试结果写到配置的文件前缀的 '_stats.csv' 和 '_stats_history.csv' 文件中.
模式三: 分布式运行
locust 除了上面两种常用的模式外,还有一种叫分布式,就是用主控机器,控制助攻机,一起执行测试。
Ⅰ.主控机器master和助攻机器slave,
同一台机器
启动主控进程,在终端中执行:
locust -f 被执行的文件.py --master
启动助攻进程,在终端中执行:
locust -f 被执行的文件.py --slave
- 注意:
- Ⅰ 助攻进程可以启动多个,在多个终端中执行启动助攻进程,就能启动多个。
- Ⅱ 主控机master和助攻机slave,启动顺序没有要求,
- Ⅲ 启动主控机master后,检测到有助攻机进程,就会显示 'Client ** reported as ready. Currently N clients ready to swarm.' N指代数量
- Ⅳ 分布式支持图形界面、无图形界面,相比而言,图形界面用的较多,因为能轻松控制所有助攻机slave一起执行;分布式执行无图像界面命令,建议先启动助攻机slave,然后再在启动主控机master时,指定命令,不然,助攻机器将可能不同时执行。
- Ⅴ 分布式在执行时,设置的total users、Hatch rate,将平均分配到各个助攻机slave中执行。
- Ⅵ 建议一台机器slave个数,不要超过cpu核数数量。
Ⅱ. 主控机器master和助攻机器slave,
不是同一台机器
启动主控机器主进程master,在终端中执行:
locust -f 被执行的文件.py --master
启动助攻机器进程slave,在终端中执行:
locust -f 被执行的文件.py --slave --master-host=主控机器ip --master-port=5557
- 注意:
- 启动助攻机器进程时,--master-host指定主控机器master的ip地址,如果不带master-port则用默认的5557端口,如果主控机器指定了端口,则这个要对应修改
- 其他,与在同一台机器上一样
想了解更多有趣,有料的测试相关技能技巧,欢迎关注柠檬班微信公众号,或在腾讯课堂中搜索柠檬班机构,观看测试相关视频。
欢迎来到testingpai.com!
注册 关于